Ammonium nitrate: Fertilizer behind many industrial accidents
Change Size
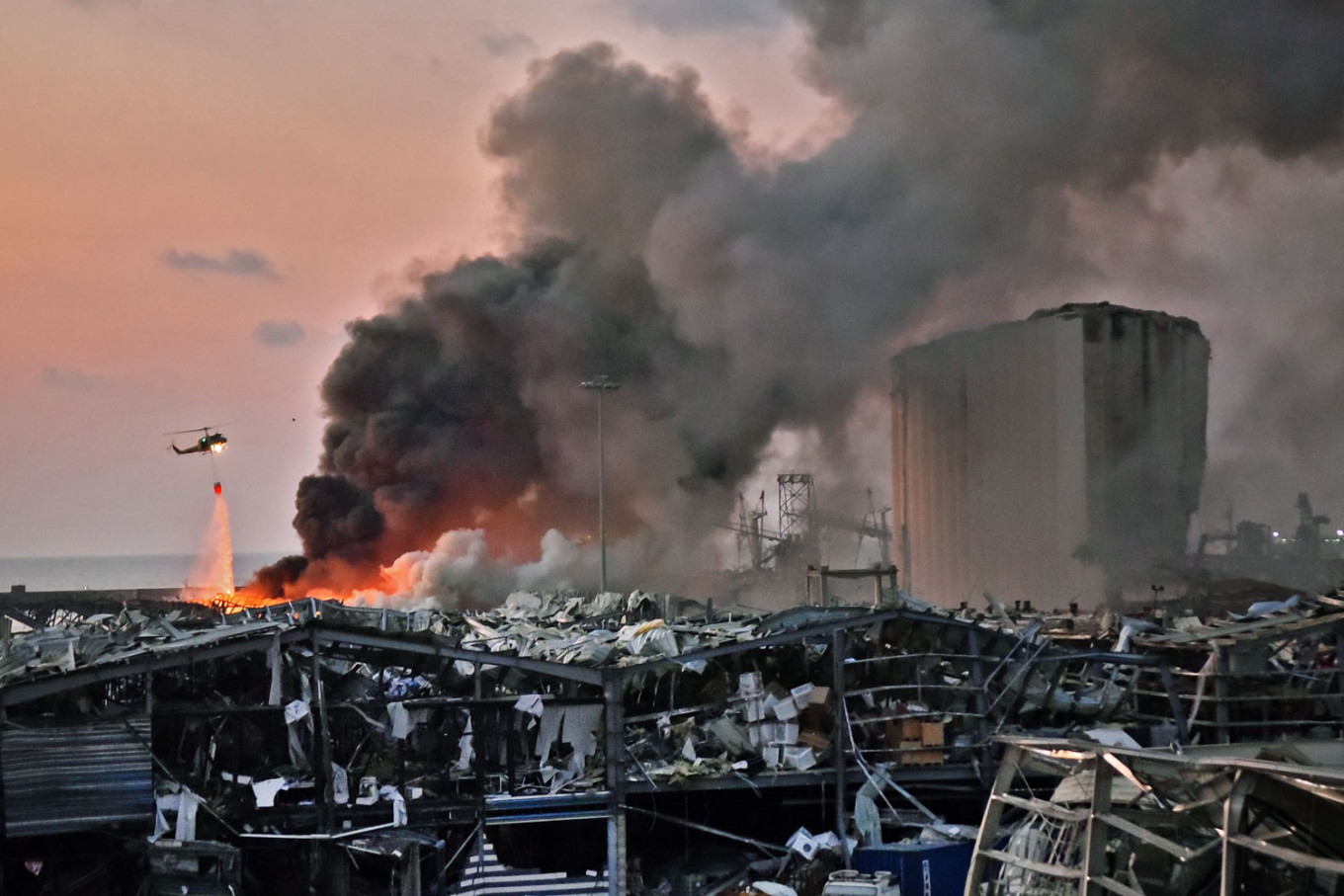 A helicopter puts out a fire at the scene of an explosion at the port of Lebanon's capital Beirut on Tuesday.Ammonium nitrate, which Lebanese authorities have said was the cause of the Beirut blast, is an odorless crystalline substance commonly used as a fertilizer that has been the cause of numerous industrial explosions over the decades. (AFP/Str)
A helicopter puts out a fire at the scene of an explosion at the port of Lebanon's capital Beirut on Tuesday.Ammonium nitrate, which Lebanese authorities have said was the cause of the Beirut blast, is an odorless crystalline substance commonly used as a fertilizer that has been the cause of numerous industrial explosions over the decades. (AFP/Str)
A
mmonium nitrate, which Lebanese authorities have said was the cause of the Beirut blast, is an odorless crystalline substance commonly used as a fertilizer that has been the cause of numerous industrial explosions over the decades.
These include notably at a Texas fertilizer plant in 2013 that killed 15 and was ruled deliberate, and another at a chemical plant in Toulouse, France in 2001 that killed 31 people but was accidental.
When combined with fuel oils, ammonium nitrate creates a potent explosive widely used by the construction industry, but also by insurgent groups like the Taliban for improvised explosives.
It was also a component in the bomb behind the 1995 Oklahoma City attack.
In agriculture, ammonium nitrate fertilizer is applied in granule form and quickly dissolves under moisture, allowing nitrogen -- which is key to plant growth -- to be released into the soil.
Lebanese Prime Minister Hassan Diab said 2,750 metric tons of ammonium nitrate that had been stored for years in a Beirut portside warehouse had blown up, killing dozens of people and causing unprecedented damage to the Lebanese capital.
However, under normal storage conditions and without very high heat, it is difficult to ignite ammonium nitrate, Jimmie Oxley, a chemistry professor at the University of Rhode Island, told AFP.
"If you look at the video [of the Beirut explosion], you saw the black smoke, you saw the red smoke, that was an incomplete reaction," she said.
"I am assuming that there was a small explosion that instigated the reaction of the ammonium nitrate -- whether that small explosion was an accident or something on purpose I haven't heard yet."
That's because ammonium nitrate is an oxidizer -- it intensifies combustion and allows other substances to ignite more readily, but is not itself very combustible.
For these reasons, there are generally very strict rules about where it can be stored: for example, it must be kept away from fuels and sources of heat.
In fact, many countries in the European Union require that calcium carbonate to be added to ammonium nitrate to create calcium ammonium nitrate, which is safer.
In the United States, regulations were tightened significantly after the Oklahoma City attack.
Under the Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards, for example, facilities that store more than 2,000 pounds (900 kilograms) of ammonium nitrate are subject to inspections.
Despite its dangers, Oxley said legitimate uses of ammonium nitrate in agriculture and construction has made it indispensable.
"We wouldn't have this modern world without explosives, and we wouldn't feed the population we have today without ammonium nitrate fertilizer," she said.
"We need ammonium nitrate, we just need to pay good attention to what we're doing with it."