Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsBuilding resilience under high external pressures
Hence, prioritizing downstreaming and industrialization can enable Indonesia to take full advantage of its resources and boost economic growth. This strategy, however, will require substantial investment in infrastructure, technology, human resources and a supportive policy environment.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
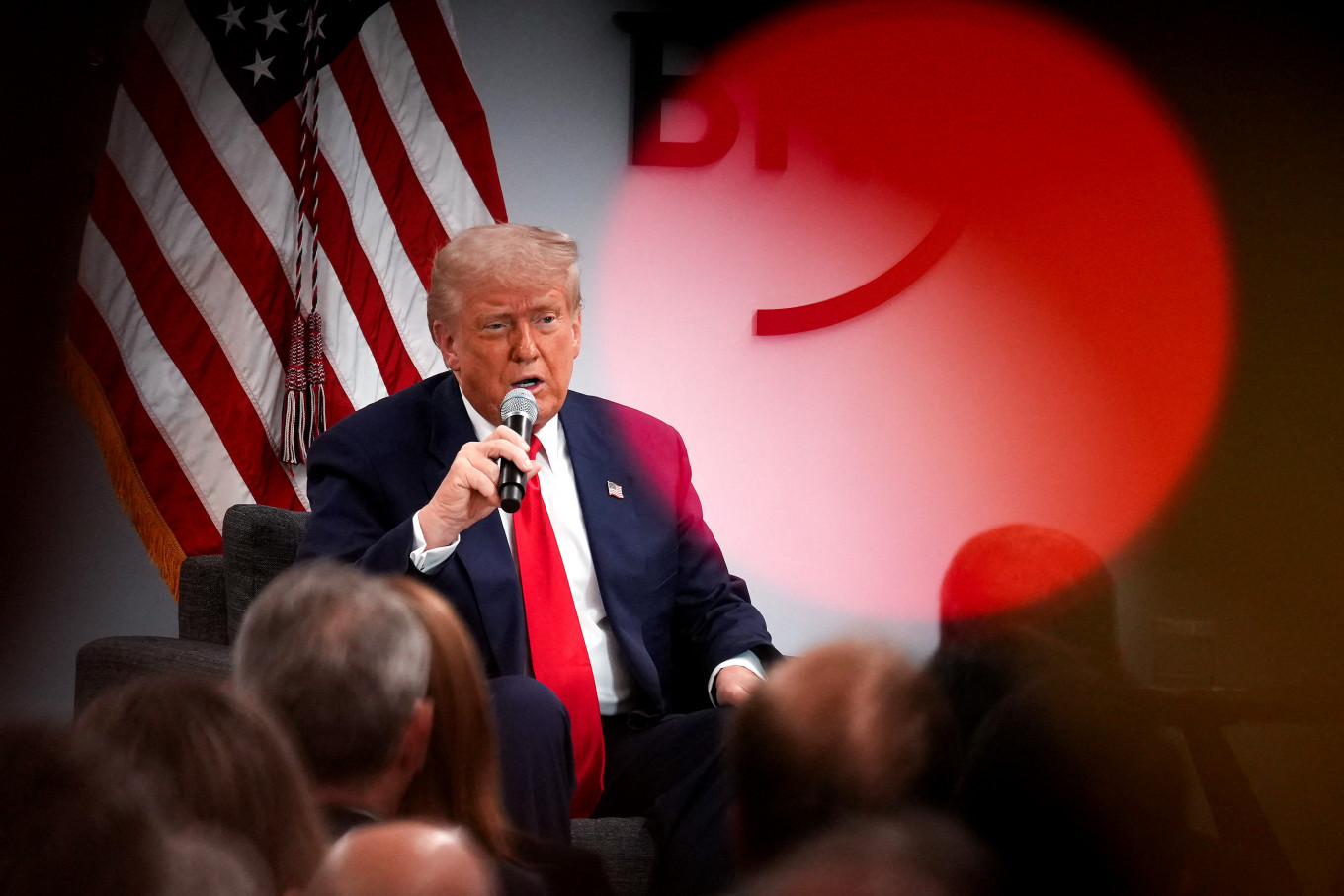 United States President Donald Trump delivers remarks at the Business Roundtable's quarterly meeting at the Business Roundtable headquarters on March 11, 2025, in Washington, DC. Trump addressed the group of CEO’s as his recent tariff implementations have sparked uncertainty that have helped fuel a market sell-off. (AFP/Getty Images/Andrew Harnik )
United States President Donald Trump delivers remarks at the Business Roundtable's quarterly meeting at the Business Roundtable headquarters on March 11, 2025, in Washington, DC. Trump addressed the group of CEO’s as his recent tariff implementations have sparked uncertainty that have helped fuel a market sell-off. (AFP/Getty Images/Andrew Harnik )
Global market volatility is increasing in response to the United States tariff policies.
US President Donald Trump announced an additional 10 percent tariff on imports from China, which has been enforced since early March. Previously, Trump had also imposed a 10 percent tariff in early February to pressure China regarding trade, technology and investment issues. Furthermore, still in March, a 25 percent tariff will also be imposed on imports of goods from Canada and Mexico. The US president also warned that there would be a reciprocal tariff policy against other countries that the government considers detrimental to US companies through significant trade barriers or higher taxes.
Prospective US fiscal policy has caused the US Treasury yield to remain high. However, it has decreased slightly because of the increasing demand of global investors for US Treasury securities, indicating capital flight to the US Treasuries.
The US tariff policy significantly impacts the global market, especially in countries that are its main trading partners. Countries affected by the higher US tariff have also retaliated, indicating rising global trade barriers. This series of events marks the beginning of the trade war, which will affect the global economy.
Trade war and trade tension will create uncertainty in the worldwide market, harming investment and economic growth. Higher import tariffs can push up inflation in other countries because companies have to pay more for imports, and these costs are often passed on to consumers at higher prices. As a result, people's purchasing power could decrease as a result of higher prices. Furthermore, higher tariffs can make it challenging for global industrial activity to compete, leading to factory closures and increasing unemployment.
The potential for higher inflation in the US could delay the Fed's interest rate cut. The Fed may hesitate to cut interest rates when inflation is high because cutting interest rates can spur demand and increase inflation. Concerns about high inflation appeared in the statement of most Federal Reserve officials who indicated no rush in lowering the benchmark interest rate, the Fed Funds Rate, this year. As a result, the US dollar exchange rate has strengthened against several major currencies.
The strengthening of the US dollar as a haven currency is shown by the increase in the US dollar index to 107-108 in recent weeks. This can also be perceived from the appreciation of the US dollar compared to other major world currencies such as the euro, the British pound and the Japanese yen. The Fed's move to maintain its benchmark interest rate of 4.25 to 4.50 percent at the beginning of this year is a response to rising US inflation expectations.