Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsWhy go back to the Moon?
It was the height of the Cold War and America needed a big victory to demonstrate its space superiority after the Soviet Union had launched the first satellite and put the first man in orbit.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
O
n September 12, 1962, then US president John F Kennedy informed the public of his plan to put a man on the Moon by the end of the decade.
It was the height of the Cold War and America needed a big victory to demonstrate its space superiority after the Soviet Union had launched the first satellite and put the first man in orbit.
"We choose to go to the Moon," Kennedy told 40,000 people at Rice University, "because that challenge is one that we are willing to accept, one we are unwilling to postpone, and one which we intend to win."
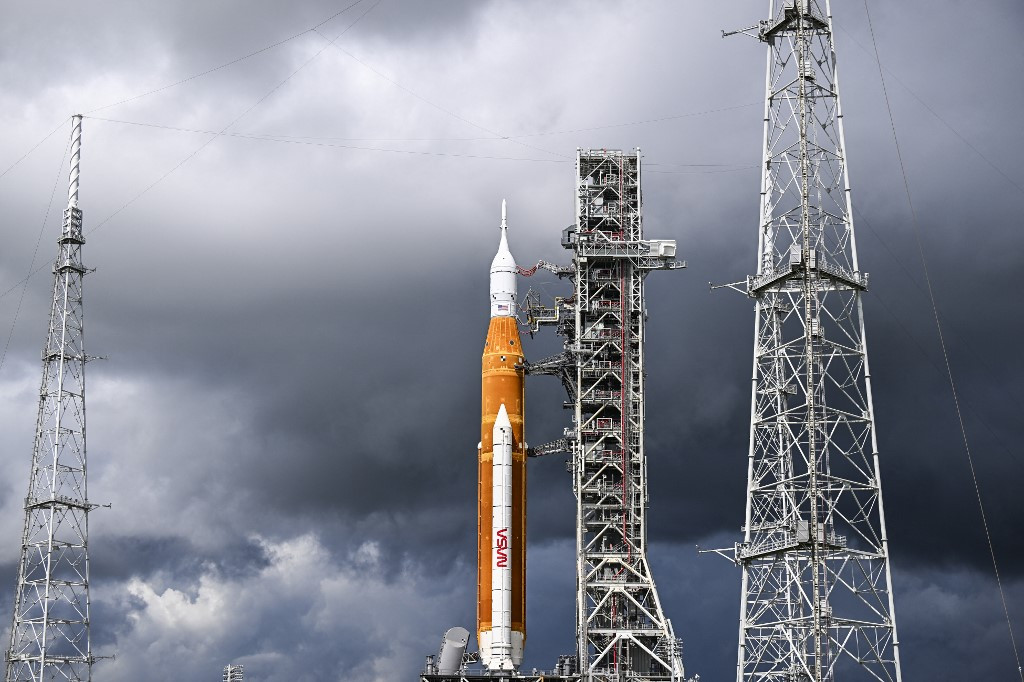
Sixty years on, the United States is about to launch the first mission of its return program to the Moon, Artemis. But why repeat what has already been done?
Criticism has risen in recent years, for example from Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins, and the Mars Society founder Robert Zubrin, who have long advocated for America to go directly to Mars.
But NASA argues re-conquering the Moon is a must before a trip to the Red Planet. Here's why.
Long space missions