Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
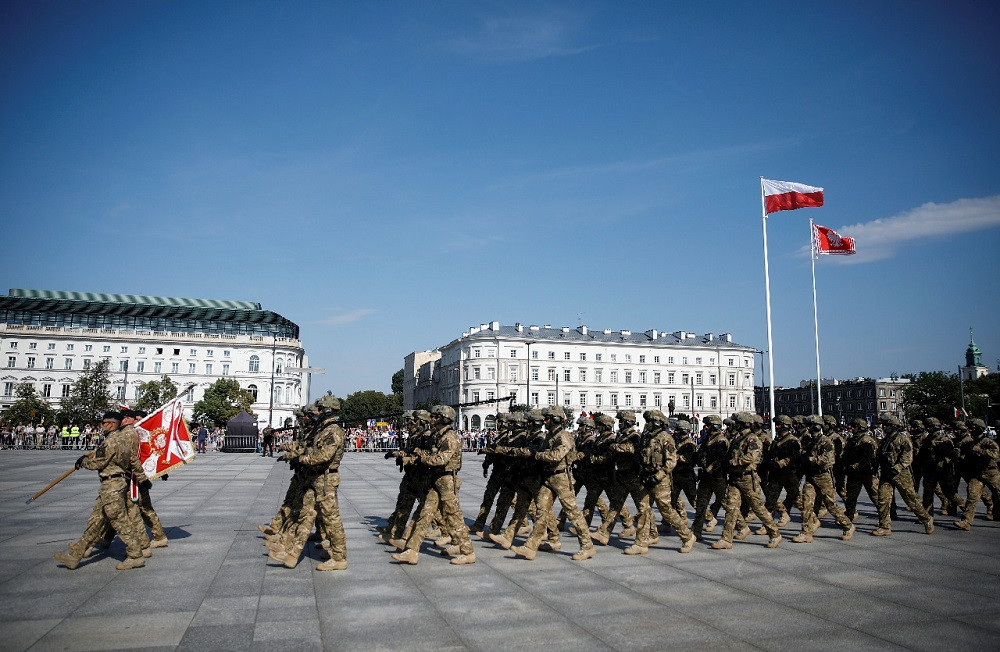
View all search resultsThe Battle of Warsaw 1920: A victory for Europe
Even though it was Poland that had won on the Vistula River, that victory concerned to a large extent the freedom of European nations from the totalitarian darkness of communism.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
T
here are crucial moments in history that define the world’s future. For Poland and Europe, one such moment in the 20th century was the day of Aug. 15, 1920. It was then that Poland, newly reborn in 1918, fought a decisive and victorious battle with the Bolshevik forces that aimed to spread the fire of the communist revolution all across Western Europe, devastated by the human and material losses of the Great War.
According to the British diplomat Edgar D’Abernon, it was the 18th decisive battle in world history. The Battle of Warsaw deserves to be listed on par with the D-Day as a critical turning point in the fight against totalitarianism in Europe.
Because of the Iron Curtain that divided Europe as a result of the Yalta Conference, the significance of this specific event to the history of Europe did not get imprinted in the world’s memory as prominently as it deserves. This concerns both mass culture and history textbooks. It is time to finally fill those gaps in European collective memory.
The anniversary of the Battle of Warsaw should be celebrated not only in Warsaw, Poland, but throughout Europe. Even though it was Poland that had won on the Vistula River, that victory concerned to a large extent the freedom of European nations from the totalitarian darkness of communism.
From a historical perspective, the year 1920 closed a series of events that began with the partitions of Poland by Prussia, Russia and Austria in the late 18th century. The Battle of Warsaw was the culmination of one of the most remarkable episodes of the building of a modern nation in European and global history. The nation without a state, emerging on the ruins of military and political defeat (including numerous Polish uprisings and collapses of successive substitutes of the state), Poland was erased from the map of Europe, which extended from the end of the 18th century to the end of World War I.
The first Polish phenomenon worth mentioning is the scale of transformation of the Polish society over 19th century from a feudal one to one of Europe’s most modern civil societies – and, as a matter of fact, without having any state institutions. An enormous network of social, cultural and sport institutions, like the “Sokół” gymnastic association, financial unions, scientific societies and school self-education societies can be compared only to reforms during the Meiji period enacted by the strong central power in Japan.
Soon after regaining independence in 1918, Poland adopted some of the most modern social and electoral legislations of the Western world. A shared sense of regained freedom prevailed over prejudice and a temptation to discriminate against wider segments of society. Poland had to build the unity and cohesion of the entire nation. The intellectual work undertaken at the end of the 19th century found its succession in the pro-state efforts once public institutions were regained after 1918.
The phenomenon of Poland is thus a story of democratization different from that in Western Europe. This is a story of democratization taking place along with the process of regaining independence and significance as a social and political entity.
This is a story of modernity being built in defiance of imperialism, absolutism and despotism of powers that dominated Europe of the 19th century. The story which found its climax in the very demanding test of maturity for the state – less than two years after it regained independence – Poland had to face a totalitarian threat from the Bolsheviks.
The war with the Bolsheviks was a demonstration of an uncommon political unity of the Polish nation. In July 1920, the government of National Defense was established, with Wincenty Witos, leader of the peasant movement, as prime minister, and Ignacy Daszyński, one of the leaders of the Polish Left, as deputy prime minister.
In light of the need to defend the very existence of the newly regained homeland, political differences among the fathers of the Polish independence receded to the background. Poland’s political elite passed the test of maturity at the most critical moment. The Polish people massively supported the war effort, with an enormous involvement of the Catholic Church.
The press called the Poles’ victory “the Miracle on the Vistula” in a clear reference to “the Miracle on the Marne” of World War I, when the French-British forces stopped the German armies.
The centennial of the Battle of Warsaw is one of the most important anniversaries of today’s free Europe. The Poles saved the West from the experience of totalitarian genocide as described by outstanding French historians in the famous Black Book of Communism. The Polish experience of communism with its tragic and long-term consequences for the country and its people is often misunderstood.
The legacy of communism is a real problem, one that deforms the social and institutional reality of the countries that underwent democratic transformation. Władysław Reymont, the great Polish novelist and laureate of Nobel Prize in Literature, in his novel The Revolt (Polish: Bunt), which he wrote following the Battle of Warsaw, presents an allegory of a revolt raised by animals against man and, parallel to this, he portrays totalitarian mechanisms.
The Battle of Warsaw was also a culmination of more than five decades of Poland’s grassroots democratic revolution, one of the most unusual and unwritten histories of Europe of the second half of the 19th century and early 20th century. It is a story of great patriotism, religious devotion, military genius and the significance of ciphers.
The Polish-Bolshevik war was a founding moment for modern Poland and a crucial moment for the entire Europe, even though the awareness of this may be insufficient. It was the real clashing point of two diverse civilizations, and no one knew it better than Karol Wojtyła, born in 1920, who would later become John Paul II: “Since the day I was born, I’ve been greatly indebted to those who then took up the fight against the invaders and won, paying the ultimate price.”
The obligation to repay this debt rests on us all. Today, 100 years after the victorious Battle of Warsaw, is a perfect opportunity to remind ourselves and the whole of Europe about it.
***
The writer is prime minister of Poland. The article was published concurrently in the Polish monthly Wszystko co Najważniejsze under a project realized in partnership with the Institute of National Remembrance.