Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search results[ANALYSIS] Stimulating a recovery amid the pandemic
While there was still a contraction, this realization was better than the economic growth of Q2, which amounted to minus 5.32 percent yoy.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
A
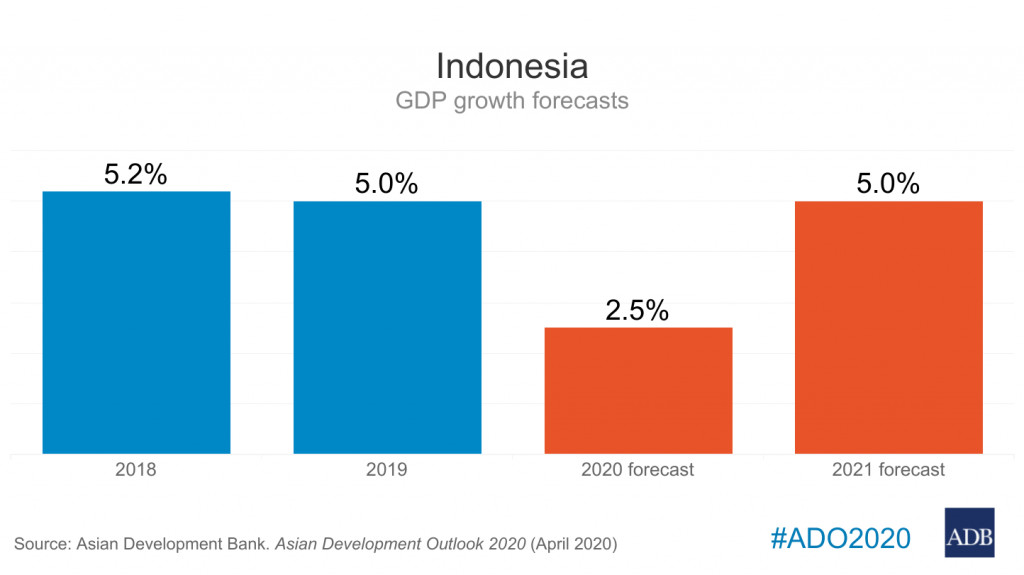
fter eight months of the COVID-19 pandemic hampering business activities and people’s mobility, the current economy is starting to show gradual improvements. Indonesia's economic growth in the third quarter of 2020 was recorded at minus 3.49 percent year-on-year (yoy).
While there was still a contraction, this realization was better than the economic growth of Q2, which amounted to minus 5.32 percent yoy.
On a quarterly basis, Q3 economic growth experienced positive growth of 5.05 percent quarter-on-quarter (qoq), improving from the previous quarter, which was recorded at minus 4.19 percent qoq.
The improvement is in line with the easing of large-scale social restrictions (PSBB), which reopened economic activity. Several recent economic indicators have also shown positive development, such as Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves at the end of October, which were still high at US$133.7 billion; controlled inflation at a low level; a healthier current account deficit; and capital inflow into the domestic financial market.
Regarding the prospects for economic growth in the fourth quarter, it is estimated that the economy will improve further so as to support optimism over the financial market and maintain the flow of foreign funds into the domestic market. Throughout November, capital inflow recorded in the stock market reached Rp 3.4 trillion ($240.69 million) and Rp 13.3 trillion in the bond market, after experiencing a total outflow of $2.25 billion during Q3.
After the decline in COVID-19 cases and the ongoing vaccine clinical trials, it is predicted that economic growth will also gradually recover in the future.
The domestic economic recovery is also influenced by the positive outlook on the global economy. Global mobility, which shows an increase and expansion of the Manufacturing and Services Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI), also occurred in the United States and China. Consumer and business confidence also improved in the US and the European region.
The declining uncertainty in global financial markets has also boosted investor optimism to invest in developing countries, including Indonesia.
This was influenced by positive expectations of the global economic outlook and the results of the US election, tow which the market responded well. Joe Biden's victory is expected to bring better policies for the US economy and international cooperation going forward.
In an effort to boost the economy and curb the risk of COVID-19, central banks in a number of countries have implemented monetary easing policies by cutting interest rates. In general, central banks in the world also monitor foreign exchange liquidity and the effects of capital flows on financial markets.
To maintain external stability in each country, intervention in the foreign exchange market is also undertaken in the event of excessive volatility.
In the November Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, the Federal Reserve will continue its accommodative policy and keep the benchmark interest rate at a level close to 0 percent for at least the next two to three years.
The Fed will make adjustments to its interest rates if the US inflation rate returns above 2 percent and the unemployment rate returns to a single digit.
This low-interest rate policy is in line with the current efforts of central banks in other countries, especially to support economic growth hit by the pandemic. The Fed's dovish policy has a positive correlation with developments in the domestic money market.
Several global market indicators also reflect market recovery. The Dollar Index has moved in a narrow range at the levels of 91-94 during the last four months, which indicates that the dollar is weakening in general against major currencies.
The current level of Indonesia's credit default swap (CDS) has decreased to a level of 89.6 from the level of 245 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in March.
Bank Indonesia (BI) has said that the stronger rupiah level is approaching 14,000 per dollar in accordance with market mechanisms supported by the capital inflow.
Short-term rupiah volatility may still occur due to technical correction and profit-taking against the appreciation in November. We predict that the rupiah will close at 14,296 per dollar at the end of 2020.
Market participants can take advantage of the current upward momentum with a prudent principle. The main risks that must be anticipated are if the COVID-19 pandemic does not end and the delay in procuring effective vaccines, which can lead to a further pandemic wave.
The fiscal and monetary policy measures that have been carried out so far must be continued to mitigate greater risks. These measures include rupiah stabilization policy, a monetary operation strategy to strengthen an accommodative monetary policy stance, accelerate the deepening of the money market and foreign exchange market through infrastructure development, implement policies to encourage micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSME) and strengthen digital finance.
To encourage national economic recovery in the pandemic era, BI continues its commitment to funding the 2020 state budget through the purchase of sovereign debt papers (SBN) from the primary market.
As of Nov. 17, the central bank has purchased SBN on the primary market through a market mechanism of Rp 72.49 trillion, including the main auction scheme, Green-shoe Option and Private Placement. Meanwhile, the realization of funding and burden sharing for public goods by BI through direct purchase of SBN reached RP 270.03 trillion.
Toward the close of 2020, we predict that the process of economic recovery will continue so that the flow of foreign funds can continue to enter the domestic market consistently.
Domestic economic fundamentals are relatively well maintained, supported by government and household spending and supported by sustainable monetary and fiscal policies. Increasing investor confidence is in line with the ongoing economic activity in other countries. Optimism for the momentum of economic recovery will affect the risk appetite of global investors.
For the authorities, a series of policies need to be continued to support the ongoing economic recovery. For market players, be selective in taking advantage of the recovery momentum to reduce volatility risks.
---------
Senior quantitative analyst at Bank Mandiri