Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
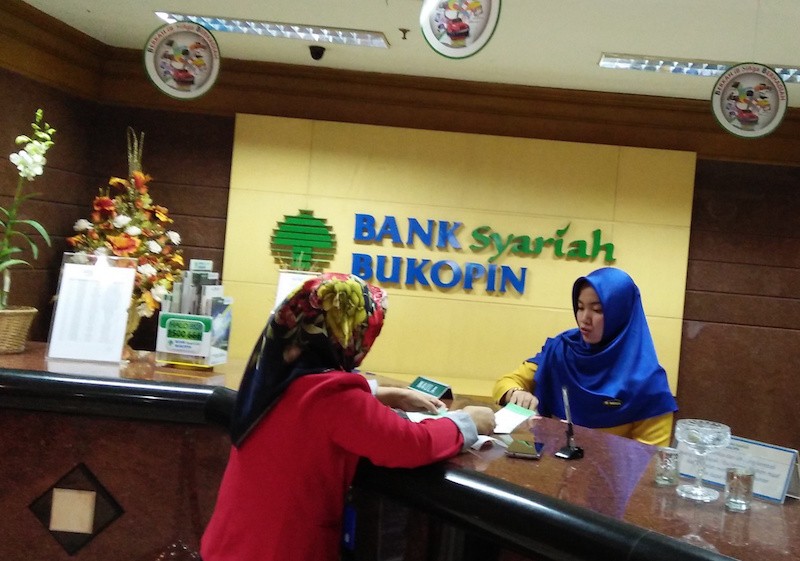
View all search resultsAnticipating new rule on sharia banks
Currently, 13 sharia banks and 21 sharia business units operate in Indonesia. With the widely differing financial strengths among banks, it appears that the decline in the statutory reserve requirement has not been strong enough to shift the lending supply curve, but had accumulated the excess liquidity of sharia banks.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
S
oon Bank Indonesia (BI) will partially apply the averaging of reserve requirement to sharia commercial banks. So far, the reserve requirement for sharia commercial banks is just 5 percent daily, with no additional 1.5 percent as for conventional banks.
Relaxing the reserve requirement will undoubtedly be good news, as the growth of sharia bank financing is slowing down. Total sharia bank financing as of September 2017 was Rp 186 trillion (US$13.8 billion), an annual increase of only 8 percent. On the other hand, third-party funds grew by 16.7 percent.
Loan growth that is not comparable with third-party funds brings sharia banks to a more elementary issue, i.e. financial intermediary function. Sharia banks are able to raise funds, but find it difficult to lend them. This is confirmed by the financing to deposit ratio indicator, which has reached more than 80 percent.
The implementation of average reserves, of course provides flexibility to sharia banks in managing their liquidity. Hopefully, a 1.5 percent portion (assuming it follows conventional banks) is streamed to buy bonds in the financial markets or lend them to small banks in the sharia-compliant interbank money market (PUAS).
Therefore, the averaging reserves can potentially increase the liquidity of the sharia banking industry by Rp 4-5 trillion. This amount is material enough to boost the financing capacity to realize the lending growth target of 12 percent.
However, the above market mechanism can occur only under conditions without any institutional constraints. In the olygopolistic sharia bank credit market, the four to five biggest sharia banks should pioneer the impact of the decrease in the reserve requirement for lending.
Currently, 13 sharia banks and 21 sharia business units operate in Indonesia. With the widely differing financial strengths among banks, it appears that the decline in the statutory reserve requirement has not been strong enough to shift the lending supply curve, but had accumulated the excess liquidity of sharia banks.