Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsOmicron less likely to cause long COVID: UK study
Researchers at King's College London, using data from the ZOE COVID Symptom study app, found the odds of developing long COVID after infection were 20 percent to 50 percent lower during the Omicron wave in the UK compared to Delta. The figure varied depending on the patient's age and the timing of their last vaccination.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
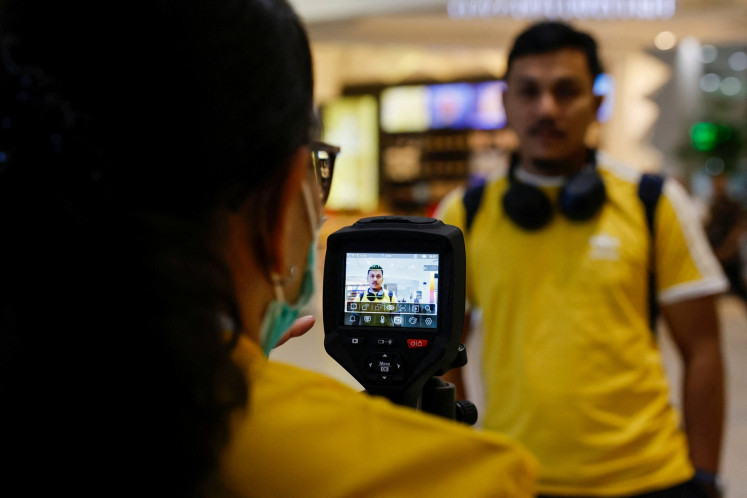
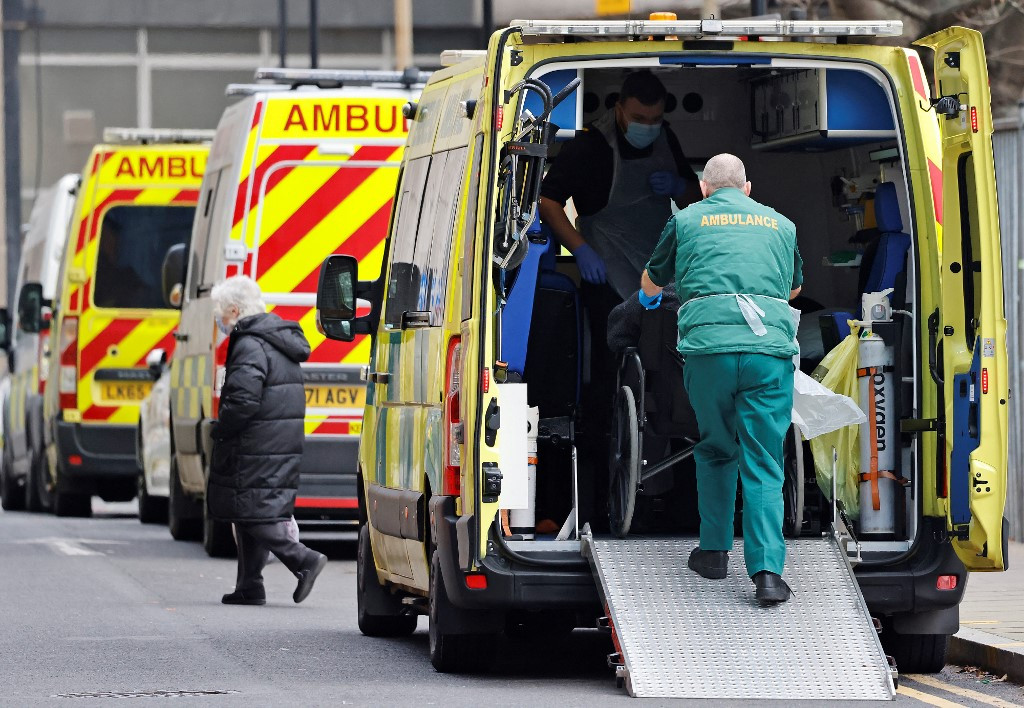 Paramedics works inside an ambulance parked outside the Royal London hospital in London on December 20, 2021. UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson on Monday faced pressure to tighten coronavirus restrictions to prevent the spread of the Omicron variant, despite opposition to do so before Christmas. The UK reported 82,886 Covid-19 cases on Sunday as the new variant rages, with the highest number of infections in London. (AFP/Tolga Akmen)
Paramedics works inside an ambulance parked outside the Royal London hospital in London on December 20, 2021. UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson on Monday faced pressure to tighten coronavirus restrictions to prevent the spread of the Omicron variant, despite opposition to do so before Christmas. The UK reported 82,886 Covid-19 cases on Sunday as the new variant rages, with the highest number of infections in London. (AFP/Tolga Akmen)
T
he Omicron variant of coronavirus is less likely to cause long COVID than previous variants, according to the first peer-reviewed study of its kind from the United Kingdom.
Researchers at King's College London, using data from the ZOE COVID Symptom study app, found the odds of developing long COVID after infection were 20 percent to 50 percent lower during the Omicron wave in the UK compared to Delta. The figure varied depending on the patient's age and the timing of their last vaccination.
Long COVID, which includes prolonged symptoms ranging from fatigue to 'brain fog', can be debilitating and continue for weeks or months. It is increasingly being recognised as a public health problem, and researchers have been racing to find out if Omicron presents as big a risk of long COVID as previously dominant variants.
The study from King's is believed to be the first academic research to show Omicron does not present as great a risk of long COVID, but that does not mean long COVID patient numbers are dropping, the team said.
While the risk of long COVID was lower during Omicron, more people were infected, so the absolute number now suffering is higher.
"It's good news, but please don't decommission any of your long COVID services," lead researcher Dr Claire Steves told Reuters, appealing to health-service providers.
The UK's Office for National Statistics said in May that 438,000 people in the country have long COVID after Omicron infection, representing 24 percent of all long COVID patients.
It also said the risk of lingering symptoms after Omicron was lower than with Delta, but only for double-vaccinated people. It found no statistical difference for those who were triple vaccinated.
In the King's research, 4.5 percent of the 56,003 people studied during Omicron's peak, December 2021-March 2022, reported long COVID. That compared to 10.8 percent of 41,361 people during the Delta wave, June-November 2021. It did not compare vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals.
While the study – published in The Lancet journal on Thursday – compared Delta and Omicron, Dr Steves said previous work had showed no substantial difference in long COVID risk between other variants.
More work was needed to establish why Omicron may have a lower long COVID risk, the team added.