Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsNew study links exposure to household chemical with heart disease, cancer
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
N
ew US research has found a link between dichlorophenols (DCPs), chemicals commonly found in a variety of common everyday products, and a higher risk of cancer and heart disease.
Carried out by researchers at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, the new study looked at 3,617 participants who had taken part in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a program of the National Center for Health Statistics at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The participants self-reported their history of illness and provided urine samples for analysis so the researchers could estimate their exposure to two types of DCPs, 2,5-DCP and 2,4-DCP.
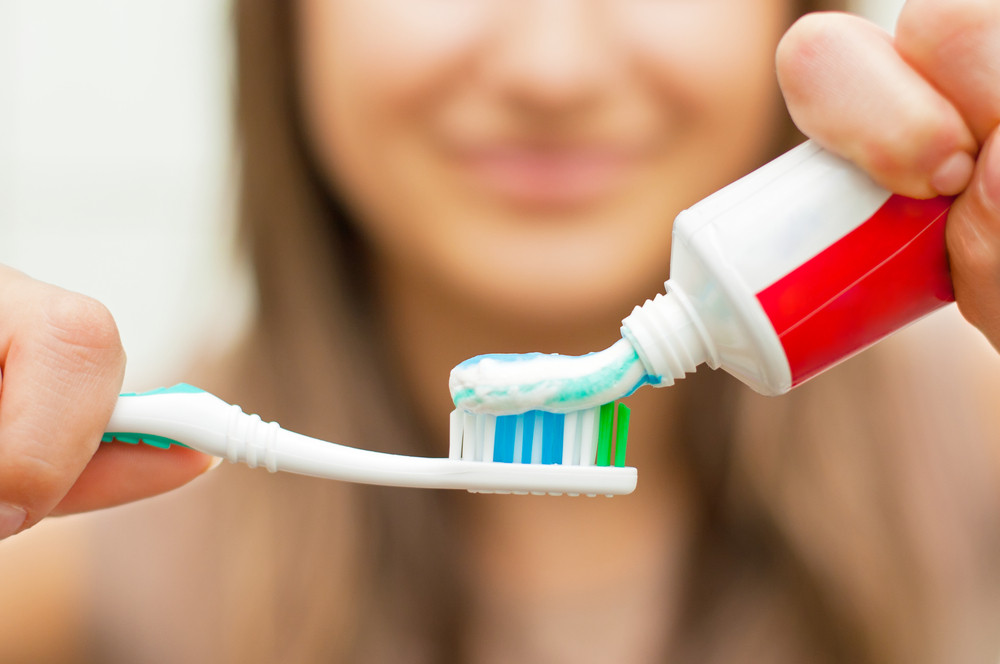
DCPs can be found in a variety of industrial and common consumer products such as deodorizers, antibacterial additives, such as triclosan, a common ingredient in toothpaste, and even chlorinated drinking water.
The findings, published in the journal Occupational and Environmental Medicine, showed that higher urinary 2,5-DCP concentrations were associated with greater prevalence of heart disease and greater prevalence of all cancers combined, however no association was found between 2,4-DCP and heart disease or cancer.
Read also: Carcinogens may lurk in these household items
In addition, no statistically significant associations were found between 2,4-DCP or 2,5-DCP and lung diseases such as asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema, thyroid problems or liver conditions.
Previous NHANES research, which showed that 81 percent of people tested positive for the presence of 2,4-DCP and 2,5-DCP in urine tests, also supports the new findings.
"Given that 81 percent of Americans show evidence of exposure to these chemicals, we need to understand more about how they may influence health," said lead author Mary Rooney.
She now recommends further research into the effects of DCP exposure.