Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsEradicating childhood TB in Indonesia by 2030
To break the transmission chain, it is essential to conduct strict contact investigations when a child is diagnosed with TB, as children often become victims of TB transmission from adults.
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
T
uberculosis (TB) continues to pose a significant health challenge in developing countries, including Indonesia, where a high burden is experienced with approximately 354 cases per 100,000 individuals, rendering it the second-highest TB-affected nation.
The situation has been further exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a rise in globally underdiagnosed TB cases. Effective mitigation necessitates enhanced surveillance methodologies, improved diagnostic techniques and heightened public awareness.
Following the recent United Nations Global Assembly to end TB, collaborative efforts and the allocation of resources will be crucial in the effort to end TB worldwide. Aligned with the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the WHO's 2025 End TB strategy, the government is determined to end the disease by 2030.
Indonesia has launched the End-TB strategy, focusing on case identification, campaigns against TB in healthcare facilities, and ensuring the distribution of treatments to affected individuals. However, achieving this goal poses a considerable challenge for a developing country like Indonesia, given the high prevalence of TB and specific circumstances that need to be overcome.
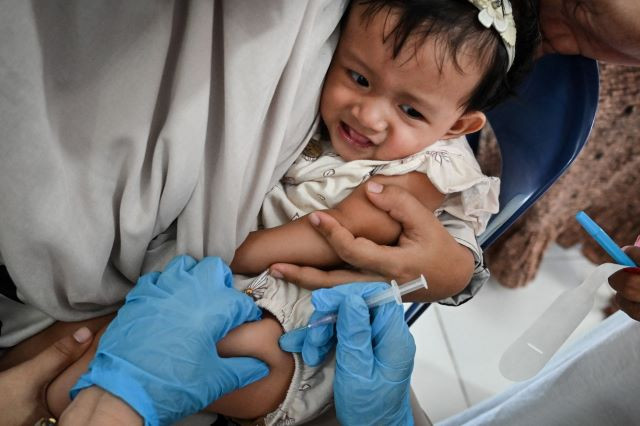
Children, as one of the at-risk sections of the population, sometimes are overlooked when it comes to TB infection. Besides chronic conditions such as adults with diabetes, HIV/AIDS and other immunocompromised conditions, children sometimes are left behind and not properly screened for the disease.
When adults are infected with TB, it implies that children in contact with them also require intervention. Close contacts, especially children under five years old, should be properly examined to make sure there is no active TB. Children who show symptoms of ongoing disease should immediately receive treatment for TB for at least six months. Meanwhile, children without signs and symptoms of TB yet in close contact should receive preventive treatment for a certain period of time.
Diagnosing TB in children presents a challenge due to distinct signs and symptoms, compared with adult patients. However, given their close contact with adults affected by TB, it is crucial to prioritize this population for attention. Undernourishment is a prevalent symptom among children with TB, and some of them may arrive at health facilities with advanced disease, leading to growth failure.