Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsAnalysis: Police reform from within: A mission impossible?
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
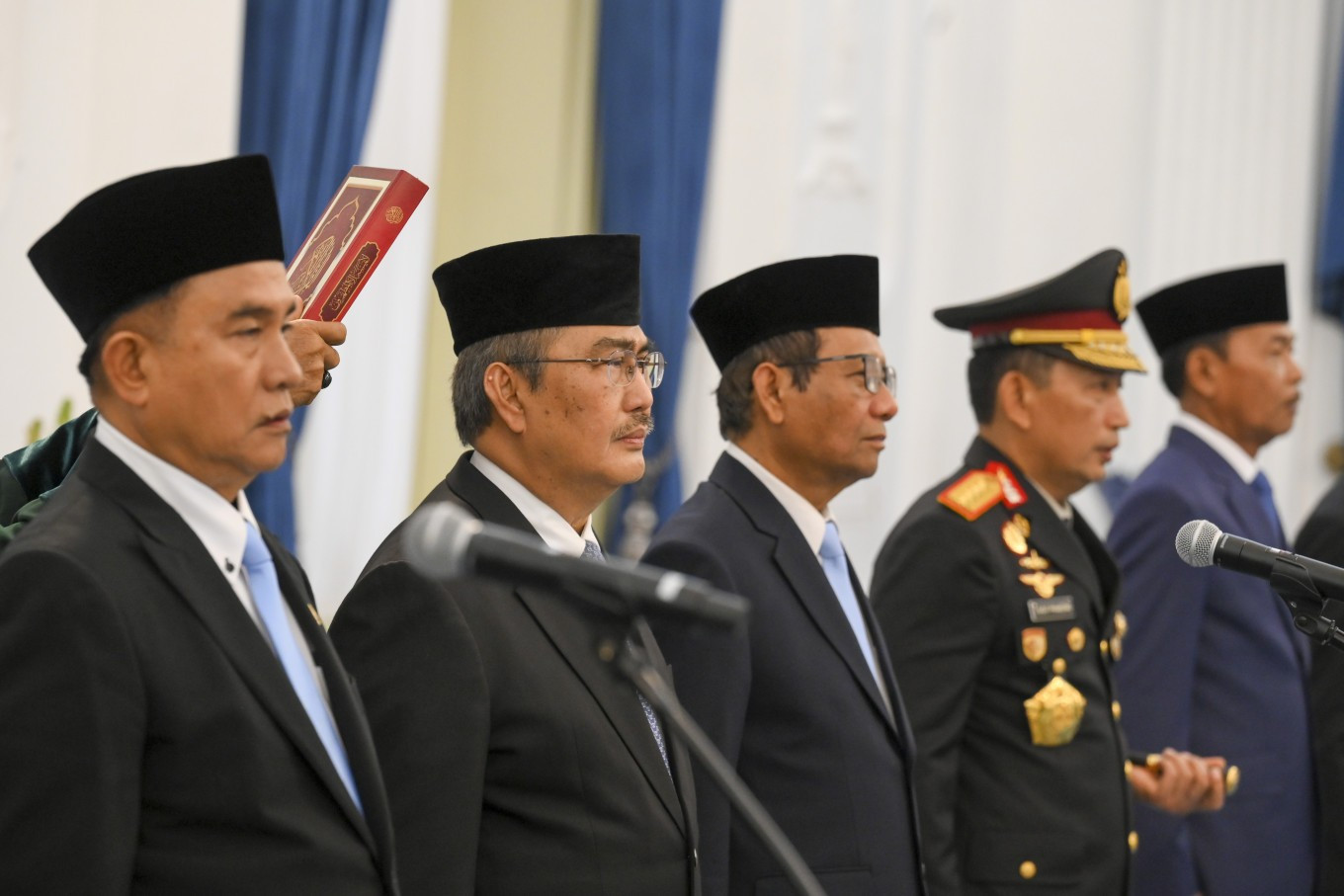 Former Constitutional Court chief justice Jimly Asshiddiqie (second left), former coordinating political, legal and security affairs minister Mahfud MD (center), Coordinating Law, Human Rights, Immigration and Correctional Services Minister Yusril Ihza Mahendra (left), National Police chief Gen. Listyo Sigit Prabowo (second right) and former National Police chief Idham Aziz attend the inauguration of members of the Police Reform Acceleration Commission on at the Merdeka Palace in Jakarta on Nov. 7. (Antara/Hafidz Mubarak A)
Former Constitutional Court chief justice Jimly Asshiddiqie (second left), former coordinating political, legal and security affairs minister Mahfud MD (center), Coordinating Law, Human Rights, Immigration and Correctional Services Minister Yusril Ihza Mahendra (left), National Police chief Gen. Listyo Sigit Prabowo (second right) and former National Police chief Idham Aziz attend the inauguration of members of the Police Reform Acceleration Commission on at the Merdeka Palace in Jakarta on Nov. 7. (Antara/Hafidz Mubarak A)
A
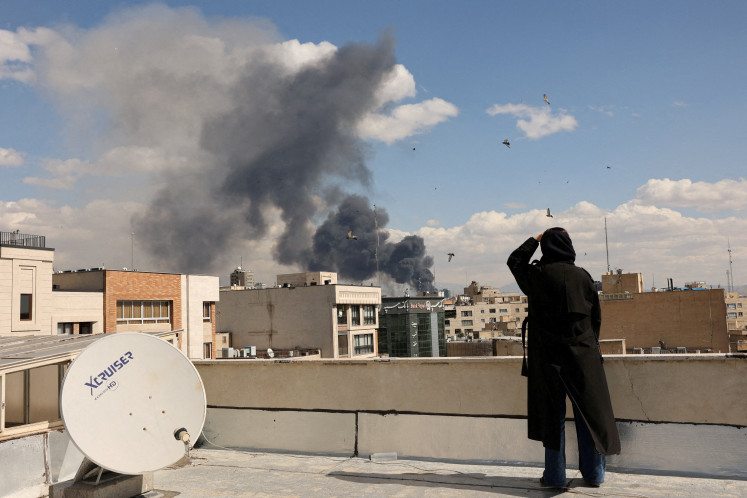
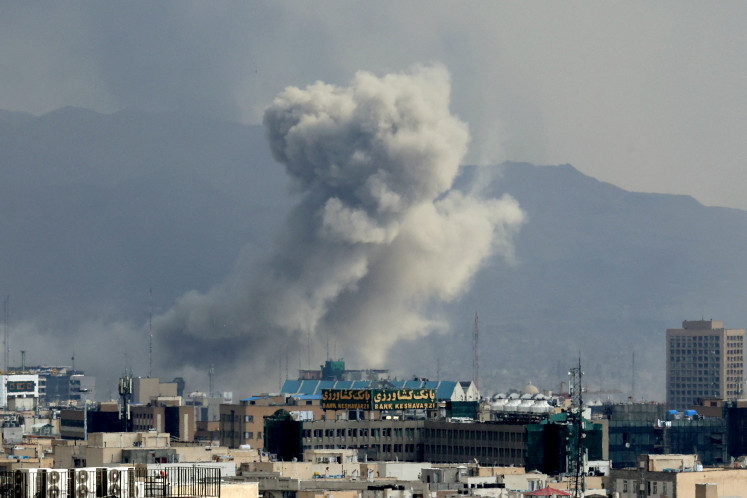
fter nationwide protests swept the country in late August, the demand for institutional police reform rose to the top of the national agenda following an incident where an armored police vehicle struck and killed a civilian during the demonstrations. Just two months later, President Prabowo Subianto responded by establishing the National Police Reform Acceleration Commission.
The new body consists of 10 individuals from diverse backgrounds that include notable Indonesian legal figures, namely former Constitutional Court chief justice Jimly Asshiddiqie, Coordinating Law, Human Rights, and Immigration and Correctional Services Minister Yusril Ihza Mahendra, and legal expert and politician Mahfud MD.
However, the body also includes National Police chief Gen. Listyo Sigit Prabowo and his three predecessors, Idham Aziz, Home Minister Tito Karnavian, and Badrodin Haiti. This has cast doubt on whether substantive changes can be achieved. Indonesian Legal Aid Foundation (YLBHI) Muhamad Isnur said that the presence of sitting and former police chiefs undermines public trust in the commission. "These are people who once led the police force and yet failed to implement many reforms," Isnur noted.
Reforming law enforcement institutions in Indonesia has always been a double-edged sword. Legally, the National Police is directly under the executive branch's jurisdiction, granting Prabowo authority to mandate changes. In practice, direct intervention carries repercussions that could destabilize his political capital.
Both the National Police and the Indonesian Military (TNI) have maintained a tradition of political involvement since the nation's inception. During the 2024 presidential election, reports from Tempo alleged that the police played an active role in securing the win for the Prabowo-Gibran Rakabuming Raka ticket, a claim both parties rejected.
Regardless, directly confronting the institution now could pose significant risks for the President ahead of the next election cycle. Curtailing police powers inevitably invites intense counter-lobbying and necessitates compromises, the inclusion of police chiefs in the reform team as an example, to ensure the institution does not lose its foothold in the national political sphere.
For the TNI, having a former army general as President has helped them maintain their standing amid the public's growing discontent with law enforcement. When journalists presented Prabowo with a list of demands in the aftermath of the August protests, he welcomed most reforms as "logical" while explicitly singling out changes to the military as "debatable".