Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsAnalysis: Prabowonomics and the political economy of scale
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
A
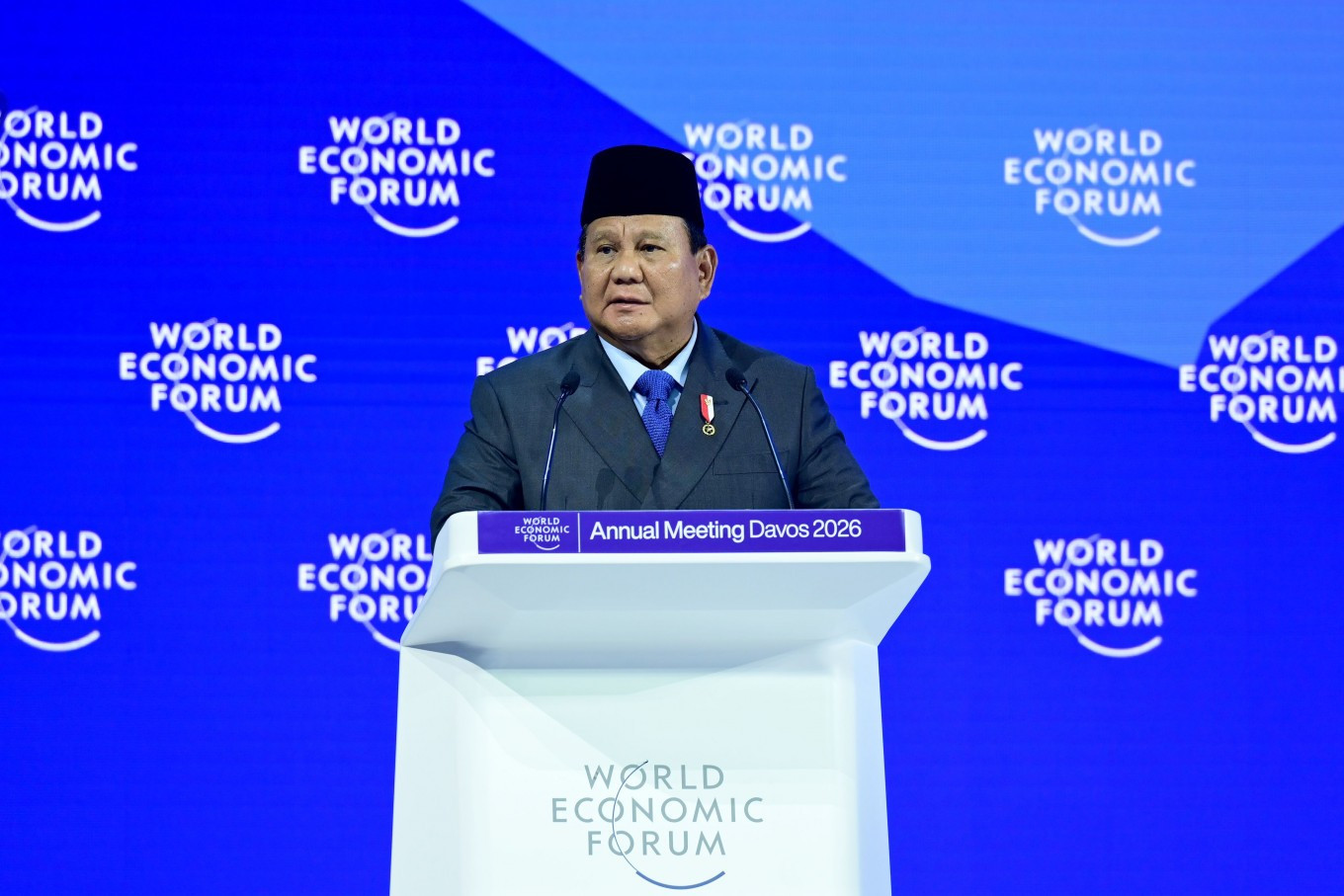
fter “greedynomics”, a new label has entered Indonesia’s political–economic vocabulary: “Prabowonomics”. The term made its global debut at the World Economic Forum, where President Prabowo Subianto presented it as the guiding framework for Indonesia’s economic trajectory. While narratives can be curated for international audiences, economic outcomes cannot be scripted. The central question is therefore not how persuasive the narrative sounds, but whether Prabowonomics reflects genuine structural progress or merely repackages ambition and political symbolism in the absence of measurable results.
The question gains urgency when viewed against Indonesia’s domestic and global conditions in early 2026. Natural disasters and renewed pressure on the rupiah have tested macroeconomic resilience, while concerns over institutional governance resurfaced following the appointment of the president’s nephew as deputy governor of Bank Indonesia, the central bank.
At the same time, escalating geopolitical tensions and tighter global financial conditions have amplified external risks. Against this backdrop, President Prabowo opted for projection rather than caution. The World Economic Forum became the stage on which he showcased what he framed as early successes of Prabowonomics, even as uncertainty continued to weigh on the domestic economy.
Prabowonomics itself is presented not as a new doctrine but as a long-standing approach pursued by Prabowo both before and after assuming office. In his speech, he highlighted Indonesia’s macroeconomic stability, pointing to average growth above 5 percent over the past decade, low inflation, a fiscal deficit below 3 percent and manageable public debt.
Yet this narrative sits uneasily alongside the administration’s own ambitions. With a target of achieving around 8 percent annual growth, maintaining growth at roughly 5 percent is neither sufficient nor transformative. The emphasis on fiscal prudence appears aimed at reassuring global markets amid concerns over a widening budget deficit and a weakening currency.
A central pillar of Prabowonomics is the free nutritious meal program, promoted both as a social intervention and a driver of economic activity. Since its launch in early 2025, the program has expanded rapidly from 190 kitchens serving 570,000 meals per day to more than 21,000 kitchens producing nearly 60 million meals daily nationwide. The government claims a success rate of 99 percent and credits the initiative with creating hundreds of thousands of jobs.
Yet behind the narrative of scale, the free meals program has become a fiscally dominant intervention. The program absorbed Rp 71 trillion in 2025 and is projected to surge to Rp 335 trillion in the 2026 state budget, accounting for nearly half of total education spending. Rapid expansion has also been accompanied by operational and governance concerns. As of Oct. 31, 2025, at least 16,000 cases of food poisoning had been reported, which authorities argued represented less than 1 percent of beneficiaries.