Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
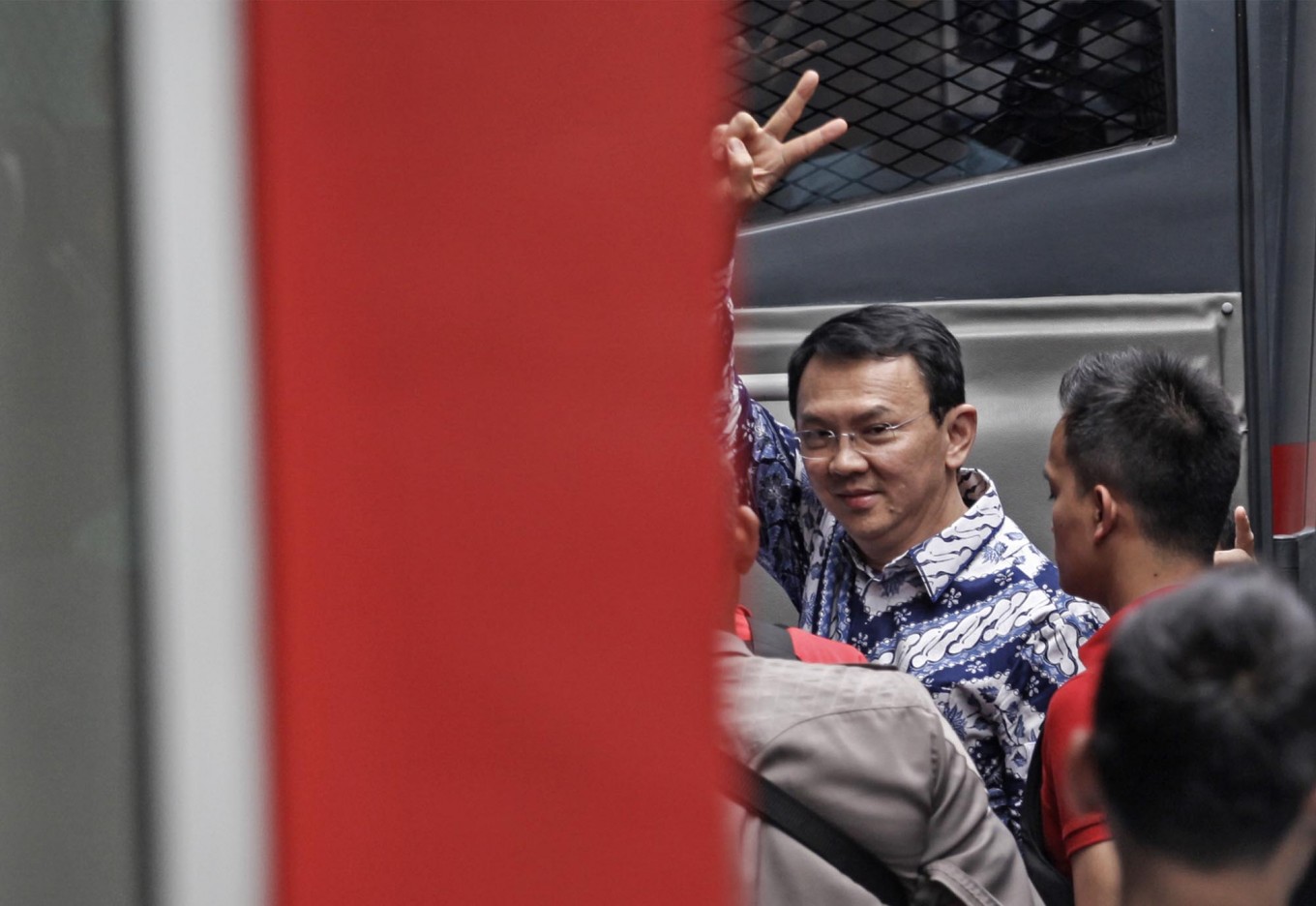
View all search resultsCommentary: Why Ahok remains a man to watch in Indonesian politics
I argue that Ahok remains one of the few people to watch in Indonesia. There are at least three reasons why
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
I
n hindsight, it may appear that Basuki “Ahok” Tjahaja Purnama has become the Kim Kardashian of Indonesian politics. Nearly a year after his upset defeat in the capital’s gubernatorial election and his controversial blasphemy conviction, the former Jakarta governor has never been completely out of the spotlight.
So it was no surprise that when news broke that Ahok had filed for divorce from his wife, Veronica Tan, the Indonesian Twittersphere went crazy.
This newspaper is obviously no place for gossiping about Ahok’s private life, but the continual limelight given to him may provide a glimpse into what lies ahead for arguably one of the most popular politicians in the country today, and why his potential comeback could change Indonesian politics in years to come.
Many would have argued that Ahok’s political career was over when hundreds of thousands of people took to the streets in Jakarta to demand his incarceration for blasphemy. That is a fair assessment, given all the doom and gloom foreign analysts repeated like a mantra about Indonesia’s dramatic turn to conservatism.
But I argue that Ahok remains one of the few people to watch in Indonesia. There are at least three reasons why.
First, his long political career has shown that Ahok is no quitter; second, his conviction, while it was undeniably damaging politically, remains widely disputed; third and most importantly, the man who became the most talked-about political figure on Twitter last year could benefit from a generational shift among Indonesian voters.
Ahok has built a stellar political career since his election in 2005 as Bangka Belitung regent. His popularity peaked when he was sworn in as Jakarta governor in 2014 to replace Joko “Jokowi” Widodo, offering a new type of leadership that has made political establishments look irrelevant at best and incompetent at worst in the eyes of voters.
True, he lost the gubernatorial election, but his defeat came after a series of rallies filled with hateful sectarian rhetoric and even death threats. The man, regardless of his flaws, did not back down, despite all the intimidation he faced.
The Chinese-Christian politician will struggle to fight the penista agama (blasphemer) stigma, but many are aware that he was a victim of an ancient draconian law. His conviction was challenged not only by human rights activists, but also a number of Muslim scholars who believed he had done nothing wrong.
Ahok accepted his conviction and dropped any legal attempts to have it overturned. This does not mean that he has admitted guilt, and if anything, it could send the right message to Muslim voters that he wanted to put the issue to rest.
That said, Ahok still has a chance to make a political comeback. And given the possible change in behavior as a result of a generational shift among Indonesian voters, Ahok could outdo many of his rivals.
According to an August 2017 survey by the Centre for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), millennials are looking for new faces in politics. Jokowi, Prabowo Subianto and Ridwan Kamil are now still the most popular presidential candidates among voters aged between 17 and 29, the survey showed.
Ahok ranks seventh after Tri Rismaharini, Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono and Gatot Nurmantyo. Of the top seven, only Ahok and Ridwan were born after 1965, have an army of online supporters and are widely seen as political outsiders.
At this point, Ridwan seems poised to grab most of the millennial votes, but pitting Ahok and Ridwan against each other is unfair at the present time, when Ridwan is running for governor in West Java while Ahok is incarcerated.
The CSIS survey would yield different results if it were carried out after Ahok had completed his sentence and launched a political campaign.
Assuming that he is granted Christmas and Independence Day remissions and is considered eligible for conditional release, Ahok could be free by this August.
Ahok has a chance to surpass Ridwan’s electability, as the former has built a political base that is ready to take on the political establishment. Ridwan’s supporters are not as militant and organized as “Ahokers,” the most prominent of whom have been consolidating and setting up a political party to contest the 2019 legislative election.
The party in question, the Indonesian Solidarity Party (PSI), is openly and aggressively trying to grab the millennial vote. The party, naturally, is filled with novice politicians with little to no experience and lacks a symbolic figure to rally support.
It is wishful thinking to believe that the political rookies in the PSI would be able to shake up patron-client politics in 2019, but Ahok could change the equation for them if the maverick politician decided to mount it as his political vehicle.
Still, millennials are notoriously unpredictable and hard to please. There is no guarantee they could be more progressive and less sectarian, but the fact is that the old voters who voted for the old parties and their old politicians will be gone soon, and the generational shift is moving voters to favoring newer parties.
The old parties are aware of the changing voting behavior, but not all of them are making an effort to adapt. It stands to reason that by 2024, Ahok and his supporters could be more prepared than others in attracting millennials, who will by then be the dominant voters.