Popular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsPopular Reads
Top Results
Can't find what you're looking for?
View all search resultsSunlight destroys coronavirus quickly, say US scientists
"Our most striking observation to date is the powerful effect that solar light appears to have on killing the virus, both surfaces and in the air."
Change text size
Gift Premium Articles
to Anyone
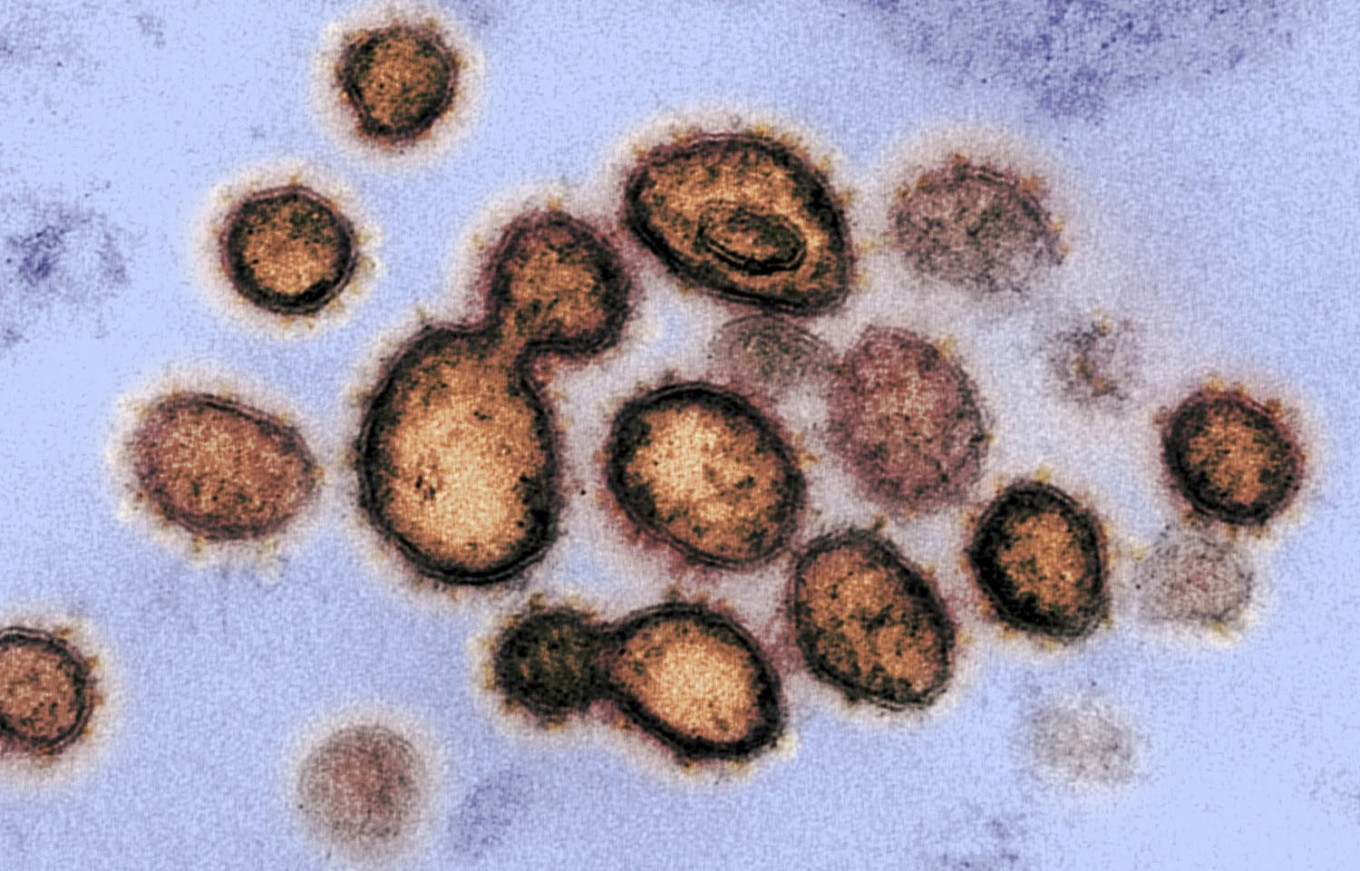 This handout illustration image obtained Feb. 27, 2020 courtesy of the National Institutes of Health taken with a transmission electron microscope shows SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, isolated from a patient in the US, as Virus particles are shown emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab - the spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, crown-like. (AFP/Handout / National Institutes of Health)
This handout illustration image obtained Feb. 27, 2020 courtesy of the National Institutes of Health taken with a transmission electron microscope shows SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, isolated from a patient in the US, as Virus particles are shown emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab - the spikes on the outer edge of the virus particles give coronaviruses their name, crown-like. (AFP/Handout / National Institutes of Health)
T
he new coronavirus is quickly destroyed by sunlight, according to new research announced by a senior US official on Thursday, though the study has not yet been made public and awaits external evaluation.
William Bryan, science and technology advisor to the Department of Homeland Security secretary, told reporters at the White House that government scientists had found ultraviolet rays had a potent impact on the pathogen, offering hope that its spread may ease over the summer.
"Our most striking observation to date is the powerful effect that solar light appears to have on killing the virus, both surfaces and in the air," he said.
"We've seen a similar effect with both temperature and humidity as well, where increasing the temperature and humidity or both is generally less favorable to the virus."
But the paper itself has not yet been released for review, making it difficult for independent experts to comment on how robust its methodology was.
It has long been known that ultraviolet light has a sterilizing effect, because the radiation damages the virus's genetic material and their ability to replicate.
A key question, however, will be what the intensity and wavelength of the UV light used in the experiment was and whether this accurately mimics natural light conditions in summer.
Virus inactivated
Bryan shared a slide summarizing major findings of the experiment that was carried out at the National Biodefense Analysis and Countermeasures Center in Maryland.
It showed that the virus's half-life -- the time taken for it to reduce to half its amount -- was 18 hours when the temperature was 70 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 24 degrees Celsius) with 20 percent humidity on a non-porous surface.
This includes things like door handles and stainless steel.
But the half-life dropped to six hours when humidity rose to 80 percent -- and to just two minutes when sunlight was added to the equation.
When the virus was aerosolized -- meaning suspended in the air -- the half-life was one hour when the temperature was 70 to 75 degrees with 20 percent humidity.
In the presence of sunlight, this dropped to just one and a half minutes.
Bryan concluded that summer-like conditions "will create an environment [where] transmission can be decreased."
He added, though, that reduced spread did not mean the pathogen would be eliminated entirely and social distancing guidelines cannot be fully lifted.
"It would be irresponsible for us to say that we feel that the summer is just going to totally kill the virus and then if it's a free-for-all and that people ignore those guides," he said.
Previous work has also agreed that the virus fares better in cold and dry weather than it does in hot and humid conditions, and the lower rate of spread in southern hemisphere countries where it is early fall and still warm bear this out.
Australia, for example, has had just under 7,000 confirmed cases and 77 deaths -- well below many northern hemisphere nations.
The reasons are thought to include that respiratory droplets remain airborne for longer in colder weather, and that viruses degrade more quickly on hotter surfaces, because a protective layer of fat that envelops them dries out faster.
US health authorities believe that even if COVID-19 cases slow over summer, the rate of infection is likely to increase again in fall and winter, in line with other seasonal viruses like the flu.